After over two years since the new version of the Google Search Console has come out, Google has finally removed access to the old version.
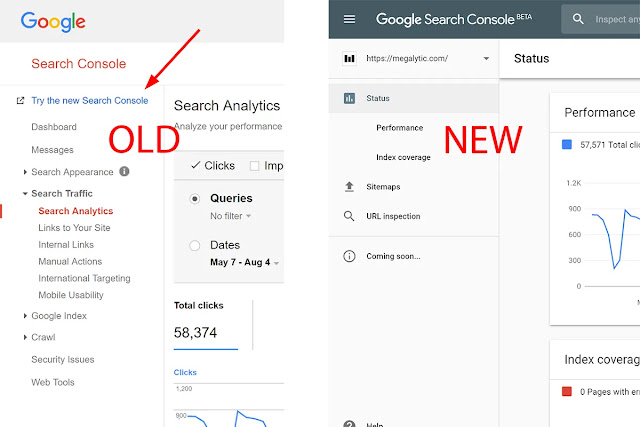 |
| Google's Old & New Search Console |
After over two years of testing the new Google Search Console and bringing it out of just about a year ago, Google has announced it has shut down the old Google Search Console.
In their Webmaster Central Blog, Google said,
Today we are reaching another important milestone in our graduation journey, we are saying goodbye to many old Search Console reports, including the home and dashboard pages 👋. Those pages are part of the history of the web, they were viewed over a billion times by webmasters from millions of websites. These pages helped site owners and webmasters to monitor and improve their performance on Google Search for over a decade.
From now on, if you try to access the old homepage or dashboard you’ll be redirected to the relevant Search Console pages. There are only a few reports that will still be available on the old interface for now - check the Legacy tools and reports in the Help Center. We're continuing to work on making the insights from these reports available in the new Search Console, so stay tuned!
The announcement also shared on the twitter account:
We’re saying goodbye to our beloved old Search Console 👋. Join us in celebrating this moment 🥳 by sharing your memories using #SCmemories - check out our tribute in the blog https://t.co/2UijlU3jLq pic.twitter.com/oD2Pf1D0qS— Google Webmasters (@googlewmc) September 9, 2019
Interface Redirect: Google is redirecting all attempts to reach the old Google Search Console into the new Google Search Console interface. There are several legacy reports that are still not migrated over or replaced in the new interface. Those reports will be accessible via an option in the new Google Search Console named “legacy tools and reports.” You will be able to access those legacy tools and reports via the links.
Google is officially sunsetting the old version of the Search Console. Users who try to access the old version will be redirected to relevant pages in the new Search Console.
There is still no 1-to-1 replacement for every old tool and report in Search Console, so Google will still be keeping these alive for now:
- Disavow Tool
- Remove URLs tool
- Crawl stats report
- Robots.txt testing tool
- URL Parameters tool
- International targeting
- Google analytics association
- Data highlighter tool
- Messages report
- Crawl rate settings
- Email preferences
- Web tools
Google will continue to work on making the above tools and reports available in the new Search Console. However, Google recently stated that users shouldn’t expect all tools to be ported over to the new version.
Below are some tools and reports which Google will be working on to make them permanent in the new search console but not all the tools will be ported over to the new version.
- Structured Data Testing Tool
- Structured Data Markup Helper
- Page Speed Insights
Currently, there are few reports from the old search console which is accessible in the New Console under Legacy Tools and Reports below Security issues and above the Links tab.
 |
| Legacy Tools And Reports In New Search Console |
In the new Webmaster Search Console, when you click the Legacy Tools and Reports, a drop-down menu displays the following items:
- International targeting
- Removals
- Crawl stats
- Messages
- URL parameters
- Web Tools
Later I'll Explain How to Use Search Console New Legacy Tools And Reports.
Google paid tribute to the occasion by gathering its team for a group photo in front of the old Search Console interface in their blog post and a tweet.
Why Webmaster and SEOs Should Care: This is a big change for a lot of SEOs who were familiar and comfortable with the old google webmaster tool interface. Google removed features slowly from the old interface, but some SEOs continued to hang on to it.
By now, we should be used to the new interface and check out the new option to see some of the legacy reports. However, Google promised to add new tools in the new search console.